Hematocrit
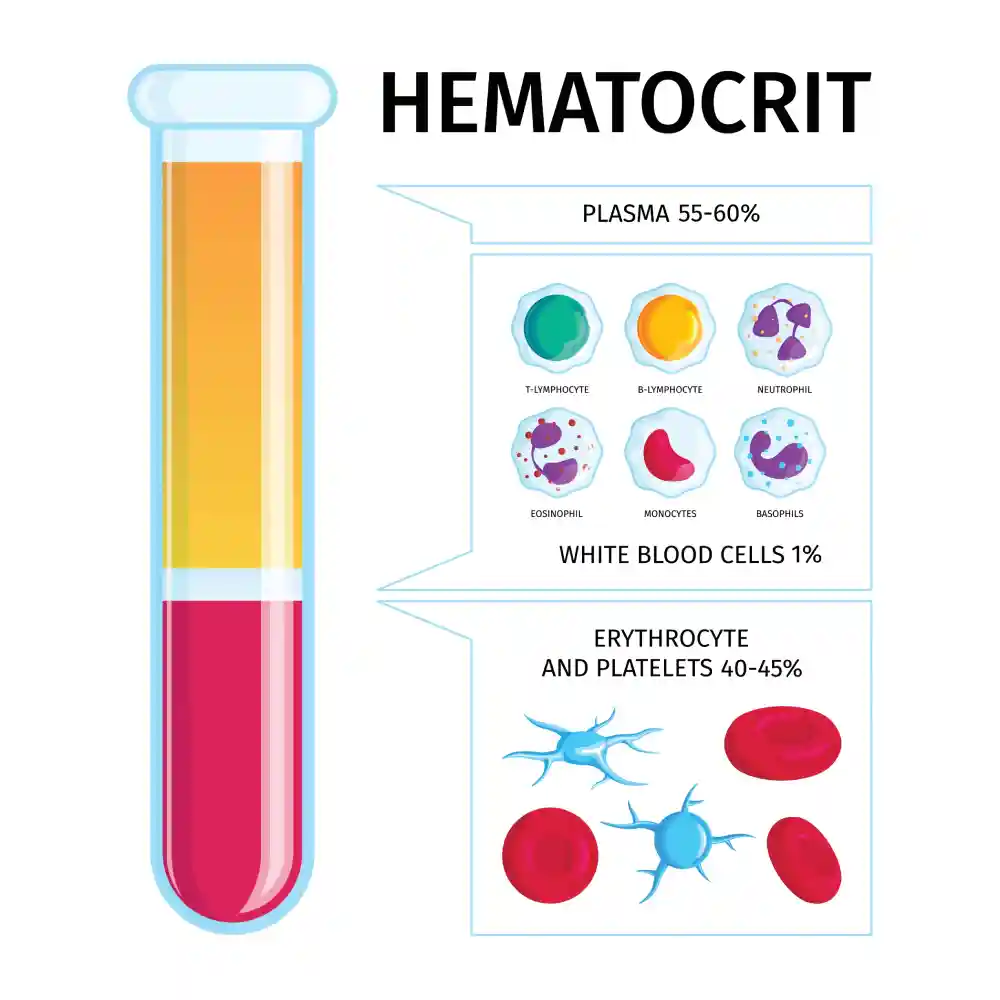
The second important value in a CBC is the hematocrit. Hematocrit is the ratio of the volume of red cells in relation to the whole volume of blood. It is a simple test but can detect anemia just like hemoglobin level. It is measured by collecting a sample of venous blood, placing it in a thin cylinder and centrifuging it which allows for cells to settle at the bottom of the tube. Red cells will be separated from the yellowish plasma and their volume can be measured.
Normal values of hematocrit are 41-50% in males and 36-48% in females and the sex discrepancy of this value is attributed to the same causes as those of hemoglobin level. Generally, hematocrit doesn’t provide much more data than hemoglobin level, but it can also be used to detect severe dehydration where its level will rise. High hematocrit also occurs in polycythemia. Hematocrit has another more important significance which is determining the mean corpuscular volume (MCV) of red blood corpuscles which will be explained later in this article.
